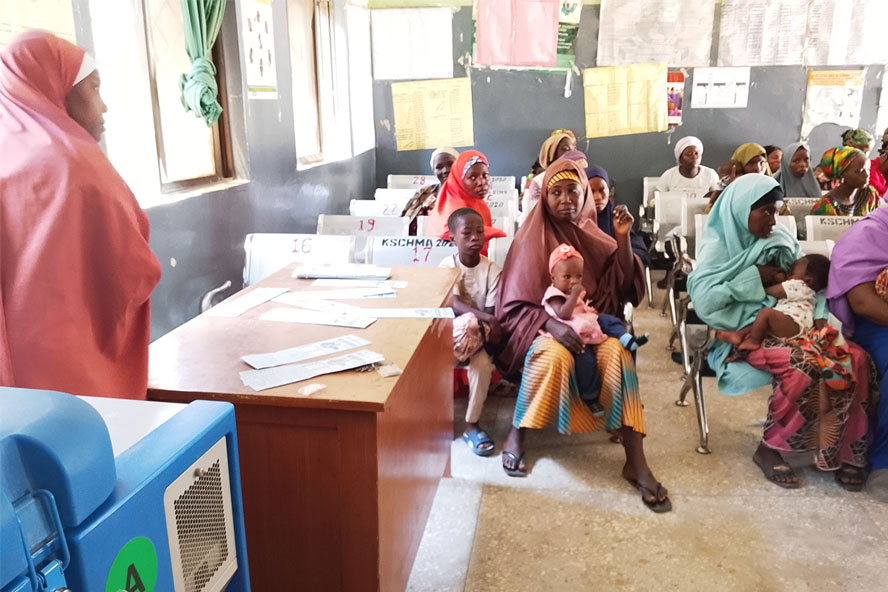
Accelerating action: the Zero-Dose Learning Hub’s 2025 in review
Gavi’s Zero-Dose Learning Hub has spent 2025 building evidence and tools that can drive immunisation progress. Here are the highlights, with resources to help move research into sustainable action.
- 17 December 2025
- 5 min read
- by JSI

Reaching every zero-dose child requires more than commitment; it requires targeted data and practical tools to drive resources where they matter most.
The Zero-Dose Learning Hub (ZDLH), established by Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance in 2022, was tasked with strengthening the evidence base on barriers to reach zero-dose children, improving metrics and methods needed to improve the reach of vaccination services, and facilitating learning exchange needed to fulfil the Immunization Agenda 2030 vision.
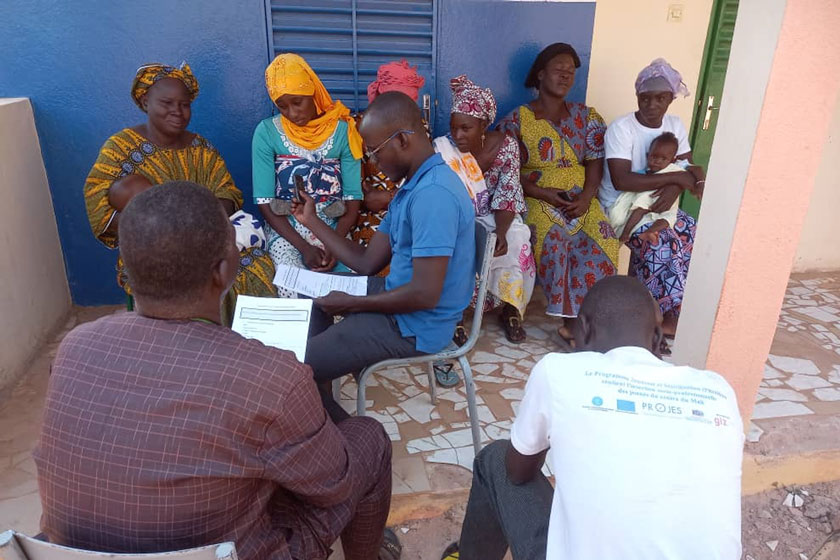
In 2025, the JSI-led ZDLH accelerated this work, synthesising empirical findings into hands-on tools and actionable findings for immunisation funders and implementers. Below you’ll find essential resources, including new costing guidance and key insights from the Country Learning Hubs in Bangladesh, Mali, Nigeria and Uganda, to help you plan smarter, target your investments and implement evidence-based approaches that make reaching zero-dose children routine and sustainable.
New tools for designing, costing, and measuring zero-dose programmes
To improve how complex immunisation interventions are designed, implemented and measured, the ZDLH published two toolkits that directly fill gaps in the global knowledge base:
- Designing and Evaluating Zero-Dose Programs with Theory-Based Approaches: A Toolkit – This resource offers guidance for designing, implementing, monitoring, and evaluating immunisation programmes targeting zero-dose children using theory-based approaches. The toolkit equips implementers and decision-makers with methods to explain why and how their programmes work (or don’t work), generating crucial evidence to improve future strategies and to guide continuous adaptation and learning. Access ZDLH theory-based evaluation resources.
- Operational Guidance: Estimating the Costs of Interventions to Reach Zero-Dose Children – This practical toolkit provides clear methods for costing zero-dose interventions. Using a transparent “ingredients costing” approach enables teams to calculate both financial and economic costs. The toolkit was designed to be accessible to programme managers, M&E specialists, and implementers with basic project management, data collection and spreadsheet skills. Access ZDLH immunisation costing resources.
Cross-country synthesis: actionable insights from four learning hubs
JSI consolidated the learnings from the four learning hubs, providing high-level recommendations to Gavi as well as national and sub-national stakeholders in two semi-annual updates (April 2025 and October 2025). Key findings highlighted in the semi-annual updates included:
- Bangladesh: Implementation research demonstrated the success of modified service schedules (like evening sessions in urban slums) and an e-screening checklist in expanding access and identifying zero-dose and under-immunised children. Annual data review also revealed an increase in high zero-dose upazilas from 227 in 2023 to 385 in 2024, signalling new hotspots.
- Mali: Implementation research on two digital tools – Coach2PEV and MEDEXIS – introduced into selected health facilities found promising potential to improve supervision and logistics systems, while also confirming persistent systemic challenges with connectivity and digital literacy that need to be resolved for national scale-up.
- Nigeria: The use of decentralised immunisation monitoring (DIM) using lot quality assurance sampling proved to be a practical and cost-efficient approach for ward-level monitoring and targeting high-priority areas for tailored zero-dose interventions. Advocacy efforts linked to immunisation accountability scorecards secured subnational financing commitments for immunisation.
- Uganda: Research on UNICEF-supported house-to-house registration highlighted that while effective for identification, follow-up systems remained weak, and the unit cost varied widely (from US$ 8.30 to US$ 68.70 per vaccinated zero-dose child across districts), emphasising the critical need for cost-effectiveness analysis before scale-up.
Accelerating evidence use: technical assistance and knowledge translation in action
The Zero-Dose Learning Hub was established to strengthen the evidence base and improve metrics across the Identify-Reach-Monitor-Measure-Advocate (IRMMA) framework and is anchored by JSI’s continuous, demand-driven technical assistance. Our role as the global learning partner is to foster a culture of collaboration and to support the learning hubs to translate their findings into action through the knowledge translation continuum.
- Technical assistance: JSI continued to provide tailored, hands-on support to the four learning hubs, including refining implementation research protocols and theories of change, strengthening data analysis and costing approaches, and guiding the publication of key evidence. This technical support culminated in the publication of the Nigeria Learning Hub’s DIM findings in Vaccines.
- From research to action – measuring knowledge translation efforts: This companion briefer to ZDLH’s Knowledge Translation Toolkit introduced practical strategies and indicators to assess whether research is reaching the right stakeholders and driving measurable change. Access ZDLH knowledge translation resources.
- Global webinars: The ZDLH hosted two global webinars focused on tailored solutions to challenges identifying and reaching zero-dose children. These sessions provided actionable insights and featured experts from the learning hubs and representatives from the Gates Foundation Zero-Dose Learning Agenda, promoting discussions on local, promising interventions. Access on-demand zero-dose immunisation learning.
Have you read?
From research to routine: leveraging ZDLH evidence for sustainable immunisation access
The critical challenge now is to continue to move these proven approaches and robust methodologies from research into routine, sustainable practice.
We invite the global public health community to leverage ZDLH’s broad evidence base. By applying these tools and country-specific lessons, policymakers, programme managers, and implementers can optimise their strategies and make lasting improvements in identifying and reaching zero-dose children and missed communities. Learn more at ZDLH.gavi.org.
The Zero-Dose Learning Hub (ZDLH)
Led by JSI, with partners the International Institute of Health Management Research and The Geneva Learning Foundation, Gavi’s ZDLH is a global learning initiative to generate evidence and engage stakeholders to identify and reach zero-dose and under-immunised children. As the global learning partner, JSI supports Country Learning Hubs in Bangladesh, Mali, Nigeria, and Uganda to advance evidence-based strategies aligned with Gavi’s Identify-Reach-Monitor-Measure-Advocate (IRMMA) framework. Key ZDLH achievements include demand-driven technical assistance and the development of tools and resources, all aimed at identifying and reaching zero-dose children and integrating evidence into policy and practice.