COVID-19 vaccination efforts prove value of polio network for resilient health systems
New report provides evidence on role of polio workforce in COVID-19 vaccine rollout and essential immunization, and makes the case to sustain the network to strengthen public health.
- 1 July 2022
- 4 min read
- by Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI)
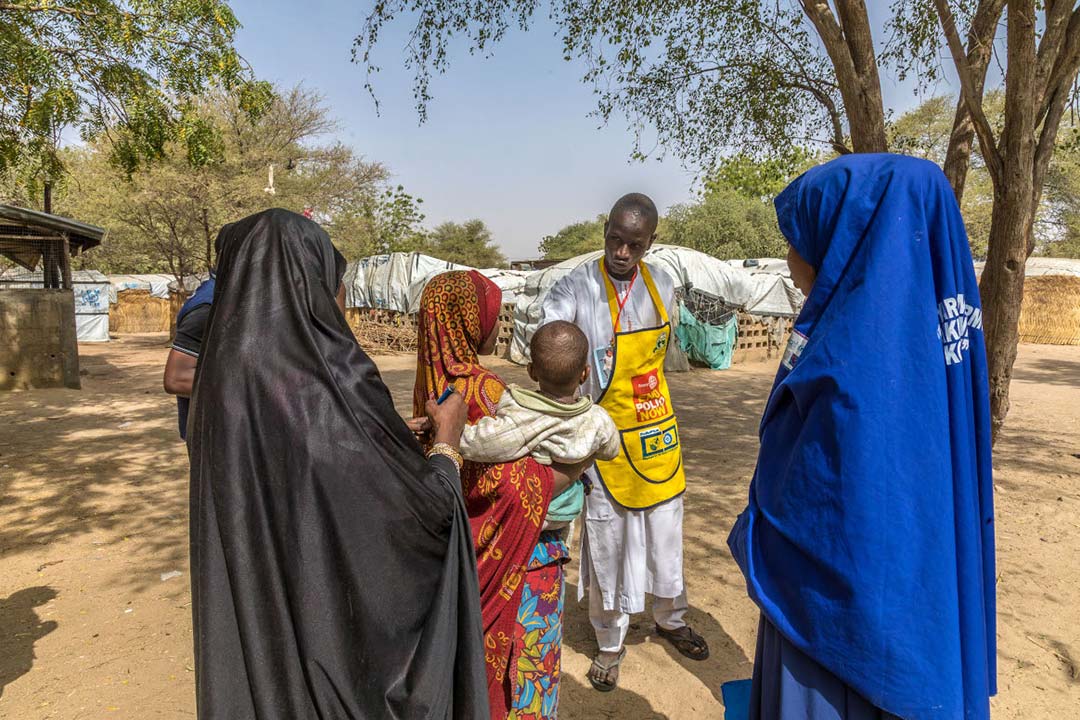

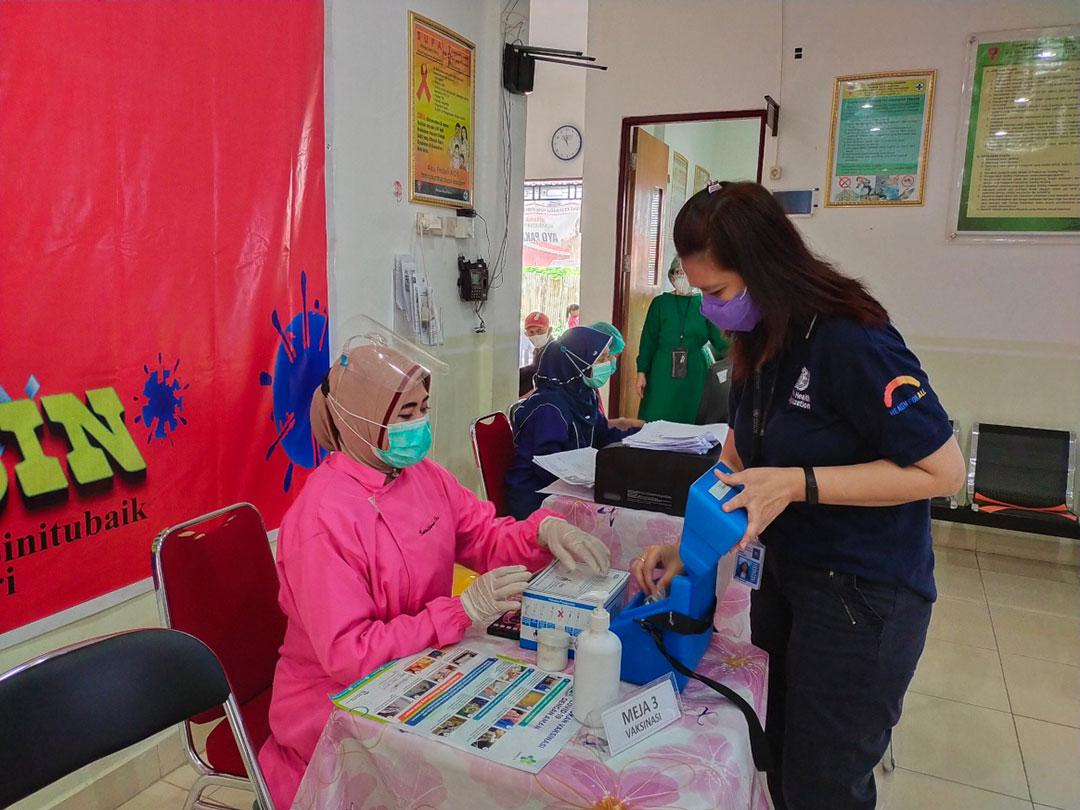
As the first COVID-19 vaccines arrived into Somalia, polio programme staff were in position. Drawing on years of experience working to tackle polio and other health threats, staff had taken on key roles in logistics, cold-chain management and monitoring to ensure the success of the vaccine rollout.
Mohamud Shire, a WHO polio eradication officer working in the central zone of Somalia, explained, “Regional and district polio officers acted as supervisors of the vaccine rollout. Some of the polio health workers worked as COVID-19 vaccinators, whereas others were social mobilizers.”
A new WHO report entitled, ‘Role of the polio network in COVID-19 vaccine delivery and essential immunization: lessons learned for successful transition’, underscores the value of the polio network as an agile and experienced public health workforce, able to pivot to support national health programmes to deliver COVID-19 vaccines, and strengthen essential immunization. The introduction of COVID-19 vaccines in 2021 stretched country health systems, requiring all hands on deck to deliver vaccines to the most vulnerable. In this challenging context, hundreds of polio eradication staff led efforts in areas ranging from coordination and community mobilization, to training and surveillance. This work proves that sustaining these capacities is the way forward to build stronger, more equitable and resilient health systems.
The polio transition process aims to sustain the workforce and infrastructure set up to eradicate polio to strengthen immunization programmes, protect against outbreaks, and deliver essential health services to communities. A 2020 report documented the outstanding contributions of the polio network to the emergency stage of the COVID-19 pandemic, with over 5900 staff in the 20 priority countries for polio transition stepping up. The new report provides evidence of the role of polio staff to support essential immunization, and makes the case to transition their valuable skills and expertise to strengthen immunization programmes, building on the COVID-19 experience.
Have you read?

© WHO/Indonesia
In Sudan, 13 polio staff coordinated with partner agencies, trained vaccinators and provided comprehensive technical support for the COVID-19 rollout. In Nepal, 15 polio and immunization officers monitored the quality of COVID-19 vaccine sessions, whilst in India, polio and immunization Open Data Kit software was used to record data from more than 450,000 COVID-19 vaccination sessions. In Nigeria, at least 121 polio staff worked to sensitize communities to COVID-19, support trainings for the e-registration of vaccine recipients, and manage Adverse Events Following Immunization (AEFI). In these countries, this work builds upon historical contributions of polio staff to essential immunization, including working with national essential immunization programmes for the co-delivery of polio with other vaccines, and using electronic surveillance tools developed for polio eradication to detect other vaccine-preventable diseases.
The report also details lessons learned from the COVID-19 vaccine rollout. One is the value of integrating polio functions into other health programmes. The pandemic response showed that with an integrated approach it is possible to achieve more with limited resources. For instance, in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, the pandemic experience has led to the introduction of Integrated Public Health Teams, which bring together public health staff to provide broader services to communities.
Another lesson is the value of transferable skills that can contribute to vaccination across the life-course. Polio personnel have specific strengths in childhood vaccination, but the pandemic has shown that their cross-cutting skills – including coordination, disease surveillance, monitoring, data management and microplanning – can be used to make progress towards global immunization goals. The pandemic has impacted rates of routine immunization, leading to an increase in numbers of un- or under-vaccinated children. Harnessing the skills of polio personnel, and integrating them into other programmes, is key to achieving the goals of the Immunization Agenda 2030.

The report further serves to emphasise that polio transition and polio eradication are interdependent, and must go hand-in-hand. In the context of ongoing polio outbreaks, the sustainable transition of functions in polio-free counties is a necessary step to ensure that health systems are resilient to future health threats, including poliovirus importations.
To support these aspects, sustainable financing for the integration and transition of polio essential public health functions is vital. As of 2022, over 50 countries have transitioned out of GPEI support, but still require funding and technical support from WHO and other partners. Long-term domestic and international support is needed to ensure that the knowledge, expertise and lessons learned from polio eradication continue to serve populations. This is especially important as governments face long-term financial constraints on their health spending due to the pandemic.
As we move towards health systems recovery, we must ensure that the polio infrastructure is transitioned in a sustainable manner, to support more resilient health systems.