Gavi aims to focus its support on the world's poorest countries and therefore bases eligibility on national income. In 2025, countries become eligible for Gavi support if their most recent gross national income (GNI) per capita was less than or equal to US$ 1,820 (according to the latest World Bank data published in July each year). Since 1 January 2011, the eligibility threshold is adjusted for inflation on an annual basis.
From the beginning of Gavi support, governments are expected to co-finance vaccines by financing a fraction of the needed doses. Gradually, as national income levels grow, co-financing levels for governments increase, as outlined in the co-financing policy.
Countries whose latest GNI per capita, or average over the past three years, falls below the threshold are classified as either initial self-financing (GNI per capita under the World Bank's low-income country threshold) or in preparatory transition (above the World Bank's low-income country threshold). These countries are eligible to apply for new vaccine support or health system and immunisation strengthening (HSIS) support from Gavi. For 2025, the eligibility threshold to enter the accelerated transition phase will be set at US$ 1,820 for both the latest and the average GNI per capita over the past three years; and the country must also contribute a co-financing share of at least 35%.
Once a country enters the accelerated transition phase, it starts to phase out of Gavi financial support over a period of eight years. Countries are eligible to apply for new vaccine support during the eight years of accelerated transition, provided that vaccine introductions during this phase effectively contribute to: strengthening routine immunisation; and increasing coverage and equity.
After eight years in the accelerated transition phase, a country becomes fully self-financing. Fully self-financing countries can no longer access new financial support from Gavi, though some types of previously approved support may continue. Several manufacturers have made commitments to continue providing these countries with access to prices similar to those Gavi pays, under specific circumstances and for a specified time period.
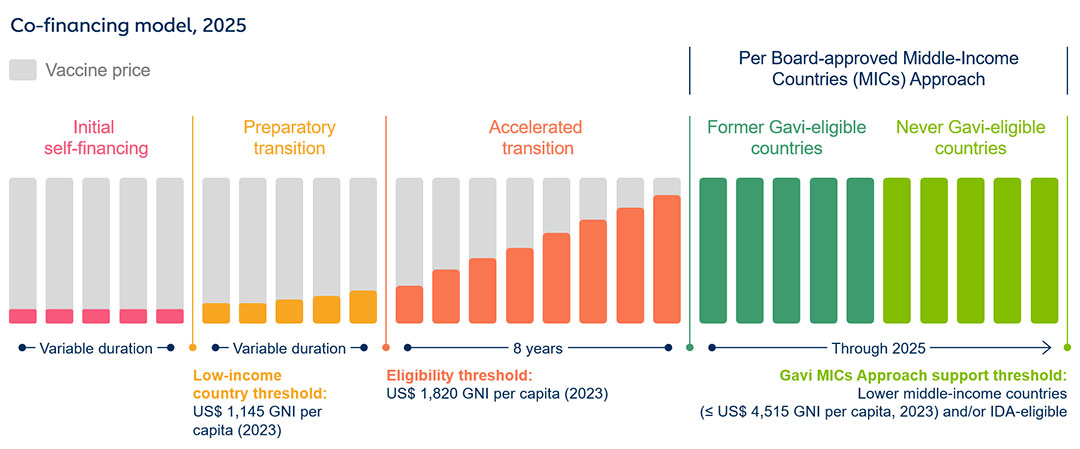
Gavi also sets specific criteria for each type of support, as outlined in the application guidelines. All country applications are reviewed by a group of independent experts in routine immunisation, health system strengthening, epidemiology and disease control, cold chain and logistics, financial and budget analysis, and gender and equity.
In 2025, 54 countries are eligible to apply for new vaccine support from Gavi:
Documents
Eligibility and transition policy
(effective through December 2025)Eligibility and transition policy
(effective from January 2026)Framework for Gavi Funding to Countries
Gavi eligibility by country
Related content
Gavi’s approach to engaging with middle-income countries
Initial self-financing
- Afghanistan
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Democratic People's Republic of Korea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gambia
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liberia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mozambique
- Niger
- Rwanda
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Togo
- Uganda
- Yemen
Preparatory transition phase
- Benin
- Cambodia
- Cameroon
- Comoros
- Guinea
- Haiti
- Kyrgyzstan
- Lesotho
- Mauritania
- Myanmar
- Nepal
- Pakistan
- Senegal
- Tajikistan
- UR Tanzania
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
Accelerated transition phase
- Bangladesh
- Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire
- Djibouti
- Ghana
- Kenya
- Lao People’s Democratic Republic
- Nigeria
- Papua New Guinea
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Solomon Islands
ELIGIBILITY SINCE 2000
In Gavi’s first phase (2000–2005), the eligibility threshold was set at US$ 1,000 GNI per capita. Seventy-four countries were initially eligible to apply for Gavi support. Timor-Leste was added to the list of eligible countries in 2002, when it became an independent state.
In Gavi’s second phase (2006–2010), country eligibility was maintained at the initial level of US$ 1,000 GNI per capita. However, the reference year of the World Bank GNI data was updated to 2003. As a result, Kiribati dropped below the threshold and became Gavi-eligible. Meanwhile, Gavi support to China and Turkmenistan, and Ukraine a few years later, concluded.
During Gavi’s third strategic period (2011–2015), South Sudan became an independent state and was added to the group of Gavi-eligible countries. In the same period, support to Albania and Bosnia and Herzegovina came to an end.
During the fourth strategic period (2016–2020), new World Bank data classifying the Syrian Arab Republic as a low-income country meant that the country became eligible for Gavi support. In this period, 16 countries transitioned out of Gavi support, bringing the number of Gavi-eligible countries by the end of 2020 to 57.
In the current fifth strategic period (2021–2025), 3 countries transitioned out of Gavi support in 2022* and none in 2023 and 2024 (due to the December 2022 Board decision to extend the accelerated transition phase from five to eight years), maintaining at 54 the number of countries eligible for Gavi support.
Since 1 January 2011, the eligibility threshold is adjusted for inflation on an annual basis. The Eligibility and Transition Policy first approved by the Gavi Board in June 2015 stated that countries’ eligibility will be determined by their average GNI per capita over the past three years. Policy updates were approved by the Gavi Board in June 2018 and December 2022; the current policy, which came into effect on 1 January 2023, indicates that either the latest GNI per capita, or the average over the past three years, must be below the threshold.
*As of 2022, 19 countries had transitioned to fully self-financing: Angola (2018), Armenia (2018), Azerbaijan (2018), Bolivia (2018), Bhutan (2016), Cuba (2018), Georgia (2018), Guyana (2017), Honduras (2016), India (2022), Indonesia (2017), Kiribati (2017), Mongolia (2016), Nicaragua (2022), Republic of Moldova (2017), Sri Lanka (2016), Timor-Leste (2018), Uzbekistan (2022) and Viet Nam (2020).

